What Changed-and Why It Matters
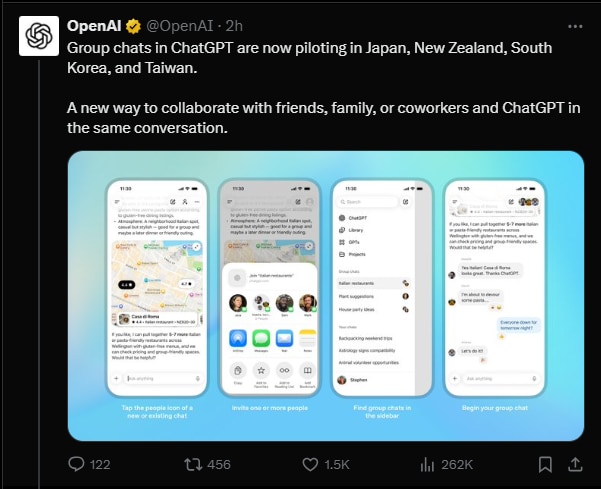
OpenAI is piloting invitation-only group chats in ChatGPT across Japan, New Zealand, South Korea, and Taiwan. It’s available on web and mobile to Free, Plus, and Team users, supports 1-20 participants, and runs on GPT‑5.1 Auto with search, image generation, file uploads, and dictation. The model decides when to speak, and usage limits and safeguards apply only when ChatGPT replies. This matters because it turns ChatGPT from a one‑to‑one tool into a live multi‑party collaborator-useful for brainstorming, triage, and classrooms-while introducing new privacy, governance, and spend‑management questions.
Key Takeaways for Operators
- Multi‑user AI: Group chats (1-20 people) let ChatGPT join conversations, respond on mention, and stay silent when not needed.
- Metering nuance: Rate limits apply only to ChatGPT’s replies, not human messages—good for flow, but expect spend spikes if groups ping the assistant frequently.
- Privacy caveat: Safety, privacy, and parental safeguards apply only when ChatGPT replies. Human‑to‑human messages may not be screened the same way.
- Capabilities: GPT‑5.1 Auto supports web search, image generation, file uploads, and dictation inside the group context.
- Pilot scope: Invitation-only in four markets; broader rollout depends on early feedback. Enterprise admin controls and retention policies are not yet detailed.
Breaking Down the Announcement
Functionally, ChatGPT can be explicitly prompted via @‑style mentions, react with emojis, and generate content personalized with members’ profile photos. Notifications trigger when ChatGPT replies or is mentioned, reducing chatter noise. Groups can switch between individual and shared threads without leaving the app, and the assistant evaluates the conversation to avoid redundant interjections.
The pilot spans iOS, Android, and the web. Early feedback will inform mechanics such as when the assistant speaks, how rate limits are enforced across participants, and whether new moderation tools are needed for group dynamics.

Operator’s Perspective: Capabilities and Constraints
For teams, this reduces friction: no more copy‑pasting transcripts into a chatbot—ChatGPT sits in the room. Examples: cross‑functional brainstorms that blend search, drafting, and image ideation; incident triage where ChatGPT summarizes threads, proposes next steps, and links references; classrooms where students co‑ask questions and the assistant alternates between silence and targeted answers.
Constraints to expect: the assistant must juggle long, branching context from multiple speakers; latency could creep up when many people talk at once; the 1-20 cap limits very large sessions. Because usage is counted only on assistant replies, a single power user can drive uneven consumption. Assign a facilitator to control mentions and consolidate prompts.
GPT‑5.1 Auto’s toolset (search, image generation, uploads, dictation) is a practical win—fewer context switches—but it also heightens risk: web search plus group prompts increases the surface for prompt injection or link‑based manipulation, and file uploads inside groups need clear data‑handling rules.
Competitive Angle
Microsoft Copilot already operates inside Teams group chats with the benefit of Microsoft 365’s established controls (e.g., tenant governance, retention, and eDiscovery). Slack AI brings summarization and Q&A to channels, and Google’s Gemini supports shared collaboration in Docs and Spaces. OpenAI’s differentiators here: inclusion of Free and Plus users in the pilot, dynamic “speak only when helpful” behavior, and metering that counts only assistant replies. The trade‑off: competitors embedded in enterprise suites typically ship richer admin, compliance, and audit features that many security teams expect by default.

Risks, Privacy, and Governance
- Scope of safeguards: Privacy, parental, and safety protections apply to ChatGPT’s outputs, not necessarily to human posts. That means user‑to‑user content could bypass the guardrails some admins assume are universal.
- Profile photo personalization: Using avatars to generate images or tailored content raises consent and brand‑use questions. Require opt‑in and prohibit likeness‑based image generation for sensitive contexts.
- Data exposure: Group uploads and search‑augmented answers can leak confidential details. Prohibit customer PII and regulated datasets; prefer synthetic or public data in pilot phases.
- Recordkeeping: Clarify whether transcripts can be exported, retained, and audited. Until policy is explicit, treat the feature as non‑system‑of‑record.
- Prompt injection and link safety: Groups increase the chance that a participant (or a fetched web page) steers the model. Train facilitators to sanitize links and pin trustworthy sources.
What This Changes for Adoption
Expect faster time‑to‑value in ideation, content drafting, and live Q&A. But regulated workflows (support cases with customer data, HR discussions, financial planning) should remain in governed platforms until OpenAI clarifies admin controls, retention, data residency, and audit options. The pilot’s inclusion of Free users is great for grassroots learning, yet it complicates centralized oversight.
Recommendations
- Run a controlled pilot (2–4 weeks) in a pilot region with 3–5 groups of 6–10 people. Assign a facilitator to regulate mentions and consolidate prompts.
- Set guardrails: no confidential or customer data; restrict file uploads to non‑sensitive materials; disable or opt out of profile‑photo personalization if unclear.
- Monitor the basics: track assistant reply counts, latency, and accuracy; spot‑check for hallucinations; create a budget threshold and an escalation process.
- Document outcomes: define when ChatGPT can decide independently versus requiring human review; capture best‑practice prompts and share them internally.
- For compliance‑heavy teams: keep this to ideation and training. For production decisions on regulated data, stick with tools integrated into your existing governance stack (e.g., Teams + Copilot, Slack with enterprise controls).
- Ask OpenAI for a roadmap: admin controls (creation, membership, export), retention and audit logs, data residency, and content filtering for all messages—not just the assistant’s.
Bottom line: ChatGPT group chats are a meaningful step toward social, collaborative AI. Early adopters will gain speed in brainstorming and coordination, but only if they manage privacy scope, prompt hygiene, and spend. Treat this as a learning pilot, not a production system of record—at least until enterprise controls are clearly defined.



